Incidence
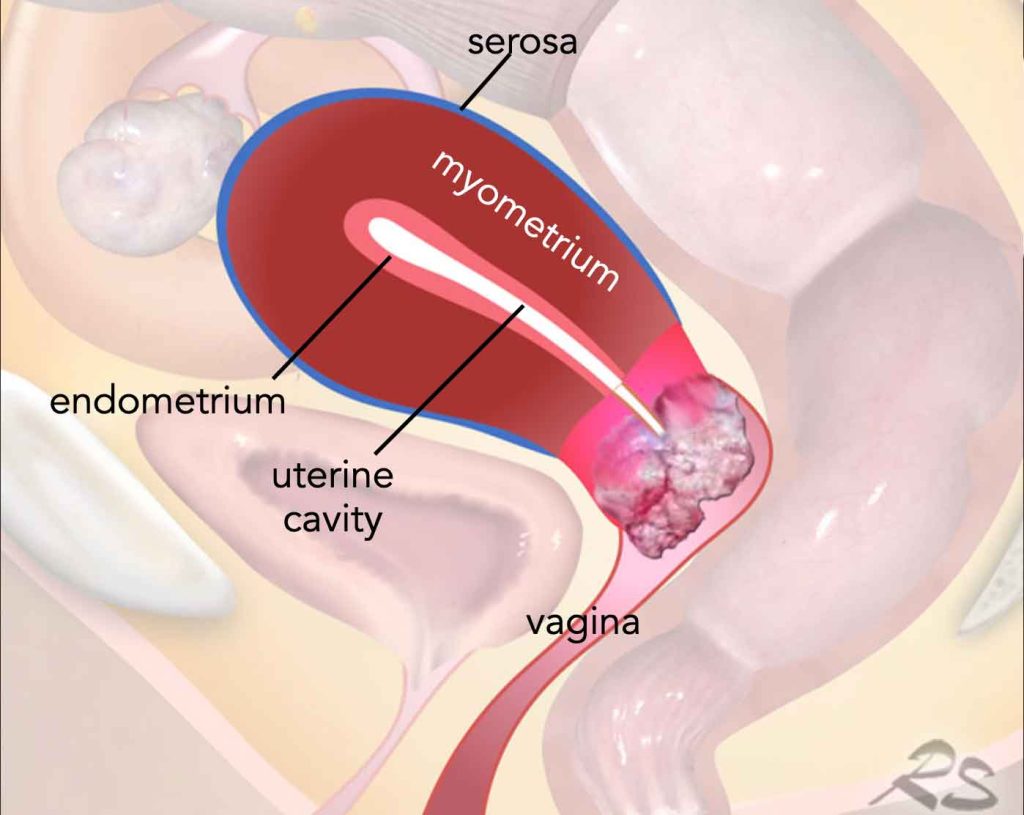
Cervix is the mouth of Uterus. Its the lowermost part of Uterus that holds the baby during pregnancy. Cervix cancer is a major public health problem in India with an incidence of 1,22,844 cases and mortality of 67,477 cases every year. Carcinoma cervix is the second most common gynaecological malignancy amongst Indian women aged between 25-44 years with an incidence of 3.5% after carcinoma breast (28.6%). It is the second most common cancer in Chhattisgarh in females. Every 8 minutes one women dies of Cervix cancer.

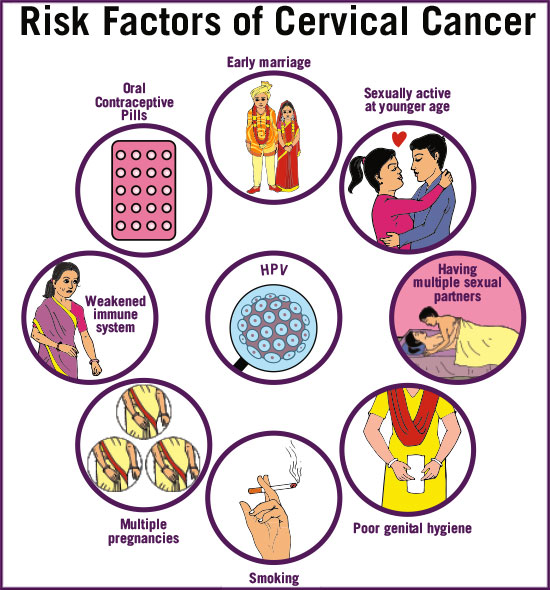
Risk factors for Cervix Cancer
- Early onset of sexual activity
- Early age at marriage
- First Pregnancy before 20years of age
- Multiple Pregnancies at short intervals. This leads to repeated injury to the cervix, leaving no time for healing.
- Sexual promiscuity i.e. multiple male sexual partners or even single male partner having sexual relations with multiple female partners
- Poor genital hygiene
- Genital tract infections with HPV(Human papilloma virus)
- Tobacco addiction
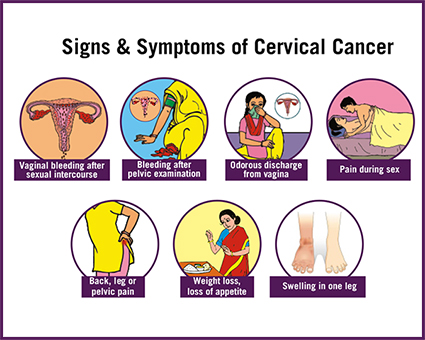
Symptoms of Cervix cancer
- Bleeding between menstrual periods(Intermenstrual bleed)
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse(post coital bleed)
- Bleeding anytime after menopause(age after which periods stop naturally)(Post menopausal bleed)
- Foul smelling vaginal discharge
- Irregular heavy menstrual periods
- Unusual blood stained vaginal discharge
- Back pain going into legs
Prevention of Cervix cancer
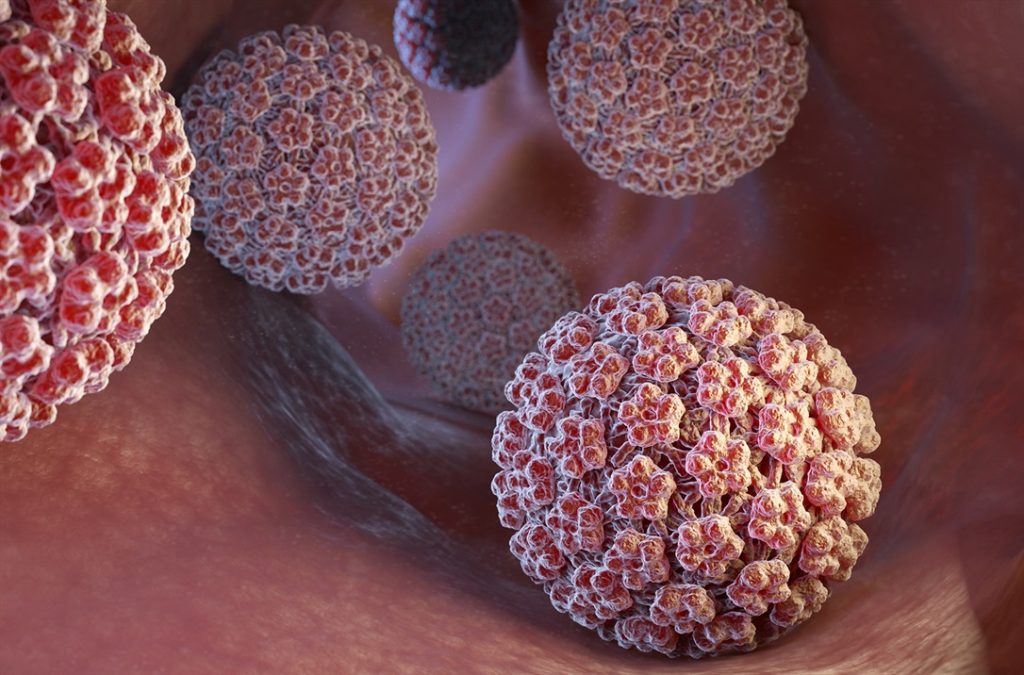
Cervix cancer is caused by a viral infection called Human papilloma Virus which enters the body of the female at the time of sexual activity. Usually 90% females are able to get rid of the virus within first two years however in 10% cases, the virus persists inside the body of the female and leads to cancer in next 10-30years. Hence, there is a long window of opportunity when the viral infection can be detected and the disease can be diagnosed in pre cancer stage.
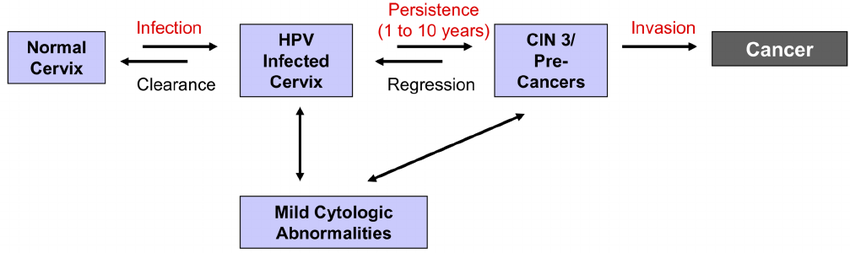
Primary Prevention(Vaccination)
The best way to prevent Cervical Cancer is to prevent virus from persisting inside the female body. This is possible through immunisation of the girls with cervical Cancer Vaccine.

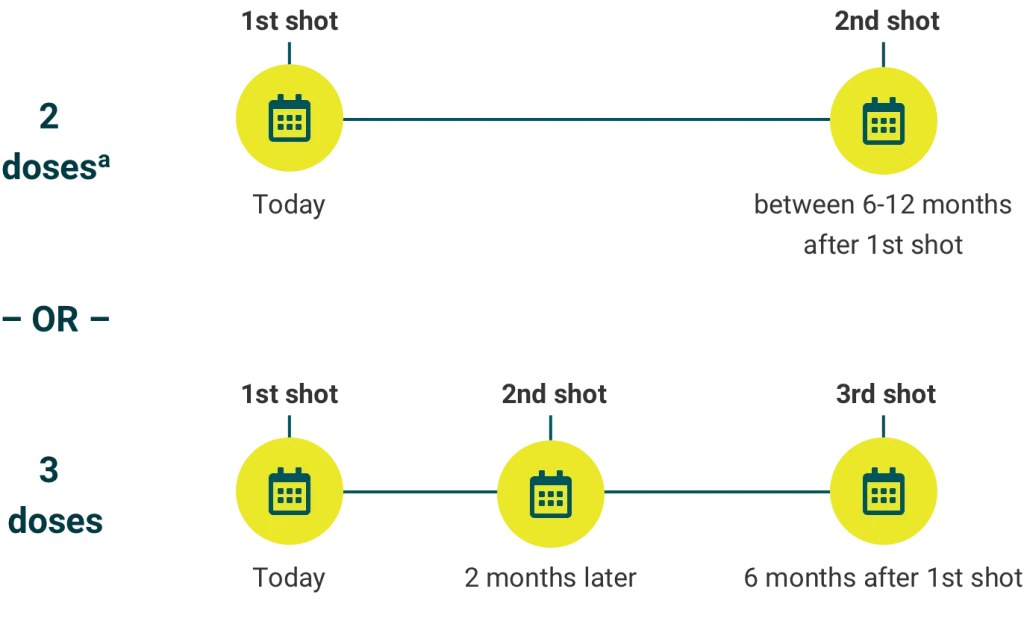
The ideal age for vaccination is between 9 to 14years for whom only two dosage of vaccine is required(0&6months). Vaccination can be given to females up to the age of 26years or those who are unmarried. These women will need three dosage of vaccine at 0,2 & 6months.
There are four types of cervix Cancer vaccines available in India
1.Cervarix ( Bivalent Vaccine)
2.Gardasil (Quadrivalent Vaccine)
3.Gardasil 9
4.Cervavac(Quadrivalent Vaccine) – Developed by Serum Institute of India
Vaccine does not have any side effect except for mild fever and injection site pain on the day of vaccination.
Vaccine is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Secondary prevention
Human papilloma Virus can be detected in females who have started their sexual activity by a test called HPV DNA test. Along with this a swab of cells is taken from cervix called Pap Smear which is sent to pathologist for microscopic examination. The pathologist can identify abnormal cells or precancer cells. This stage of disease is called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia(CIN) and can be cured with simple procedures like cauterisation.
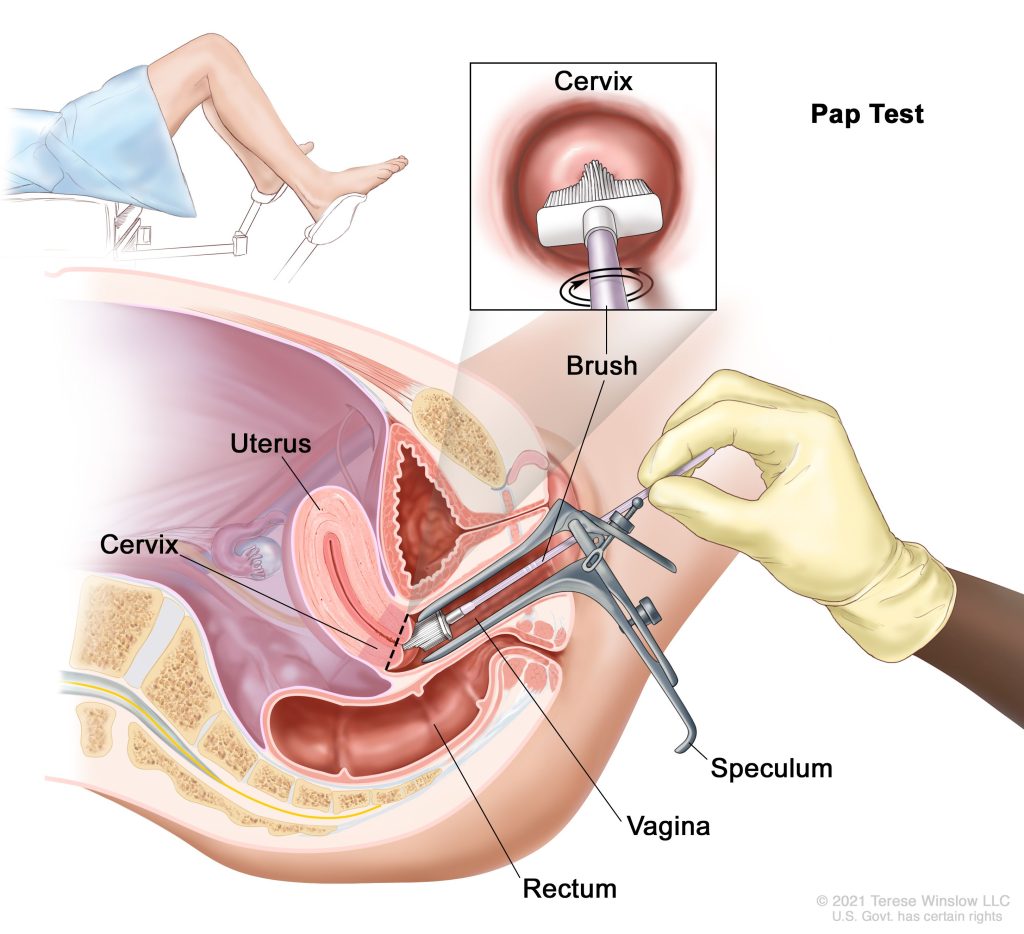
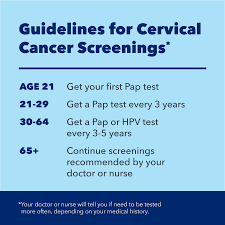
Women should get pap smear test done by a gynaecologist (lady doctor) or cancer specialist once every 5years from the age of 30yrs to 65 years.
Diagnosis of Cervix Cancer
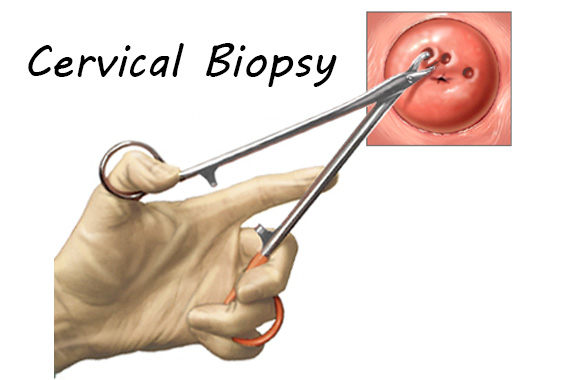
Biopsy-It helps in confirmation of the cancer. It is usually done under sedation in operation theatre.
MRI Pelvis-It helps to determine the extent of the disease into vagina and surrounding tissues
CT scan of Abdomen & chest– It helps to determine spread of the disease into surrounding lymph nodes and to other organs like Liver & Lungs.
PET CT scan– It can help determine the spread of the disease into other organs of the body like Bones, brain.
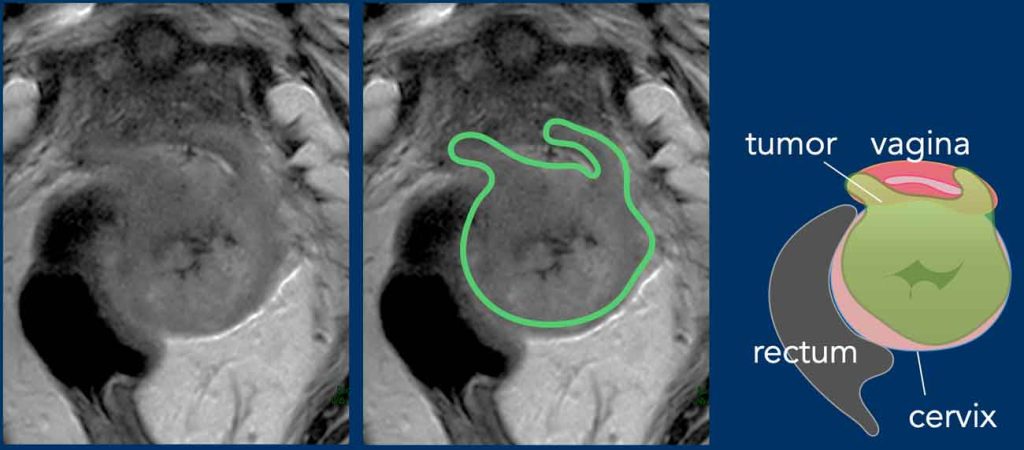
Stages of Cervix cancer
Stage I- Disease is confined to the cervix.
Stage II- Disease spreads to upper part of vagina(Stage IIA) or surrounding tissues around Uterus(parametrium)(Stage IIB).
Stage III- Disease spreads to lower part of vagina(stage IIIA), surrounding tissues compressing ureter(Stage IIIB) or Lymph nodes(Stage IIIC).
Stage IV- Disease spreads to distant organs like Lung, Liver, bones.

Treatment of Cervix Cancer
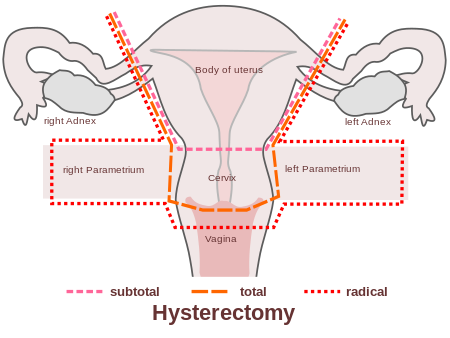
- Patients with precancer stage(CIN) can be treated just with removal of cervix or with electrocoagulation(burning with cautery) of abnormal areas.
- Patients with early stage(stage I) cancer can be treated with removal of uterus and cervix with a cuff of surrounding tissue and lymph nodes. (Radical Wertheim’s hysterectomy)
- Patients with locally advanced cancer(Stage II & III) can be treated with combination of (radical Chemoradiotherapy).
- Stage IV cancer can be treated with Chemotherapy or Immunotherapy.

Cure for cervix Cancer
There is long interval(approximately 15-20 years) between precancer stage transforming into cancer. If the cancer is detected early and treated properly then most patients can be cured of the disease.
Role of Doctors in Screening for Cervix Cancer
- Doctors should examine patients between the age of 30-65 years using visual inspection with acetic acid(VIA) who have any of the high risk factors.
- Doctors should regularly advise their patients between the age of 30-65years to get pap smear +HPV DNA test
- Doctors should counsel young girls between 9 to 26years about HPV vaccination.
Conclusion
Do not ignore symptoms of cervix cancer.
Get yourself examined today by a Cancer Specialist if there is any doubt of cervix cancer.
Getting a simple pap smear & HPV DNA test once in 5years can protect you from cervix cancer.
Get your daughters between the age 9-26 years vaccinated against HPV.

