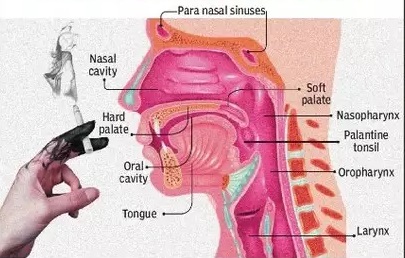
Oral cancer is the second most common cancer among males in India and third most common cancer among females in India. Approximately 15% of all cancer in males occur in Oral cavity.
Cancer of Lower jaw and cheek is the most common subsite for cancer in the Oral cavity.
Etiology
- Tobacco chewing either in the form of Pan Masala, Khaini, Gutkha, tobacco tooth powder (Gudakhu/ Misheri) or smoking cigarettes or bidi is the most common cause of lower Jaw and cheek cancer in India.
- Apart from this, alcohol consumption can also cause this cancer.
- At times, Ill-fitting dentures or sharp teeth continuously injuring the inner lining of cheek can develop an ulcer into cancer.

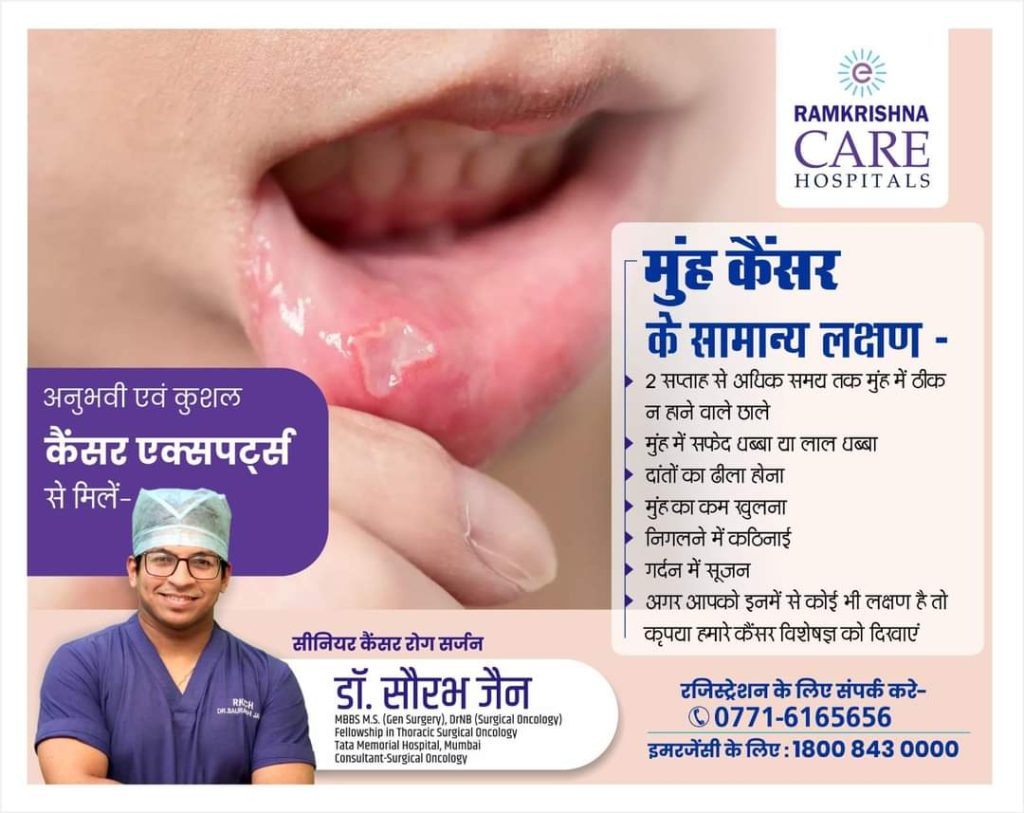
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
- Most common symptom of this cancer is non healing ulcer over lower jaw or cheek. Any ulcer that doesn’t heal in two weeks can be a symptom of Oral cancer. Apart from this, other symptoms can be
- Bleeding from gums
- Loosening of teeth
- Swelling over face/Neck
- Decreased mouth opening
Diagnosis of Oral Cancer
- When a patient comes with any of the above complaints, cancer surgeon/ specialist does thorough examination of the Oral cavity and Neck to see for clinical extent of disease and its spread into Lymph glands of the neck(manifested as neck swelling).
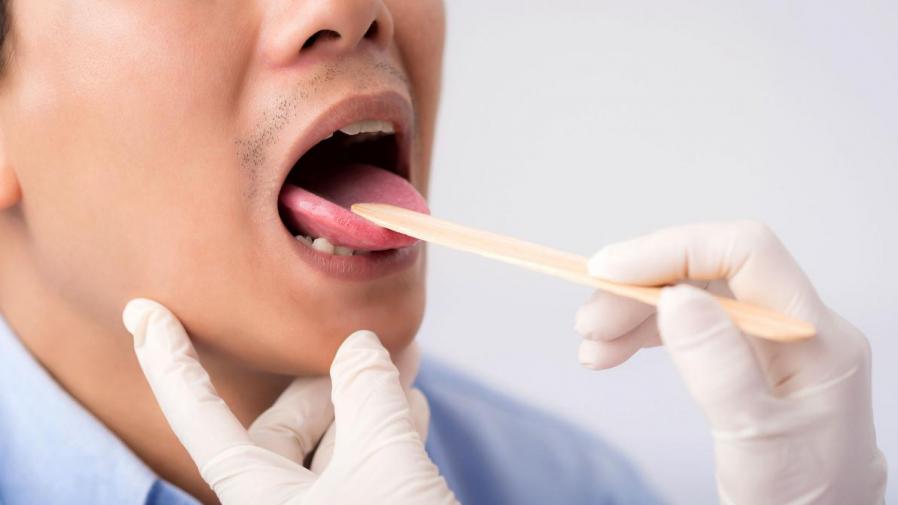
- Cancer Surgeon then takes a Punch biopsy from the lesion to confirm the diagnosis. This is done under Local Anaesthesia in the clinic itself. It’s a safe procedure. Biopsy does not increase the risk of spread of Cancer.
- After examination and biopsy, Cancer Surgeon Asks for a CT scan or MRI of the face and Neck to see for extent of disease into the bone or soft tissues of cheek and neck nodes. This helps in assessing the stage of the disease.
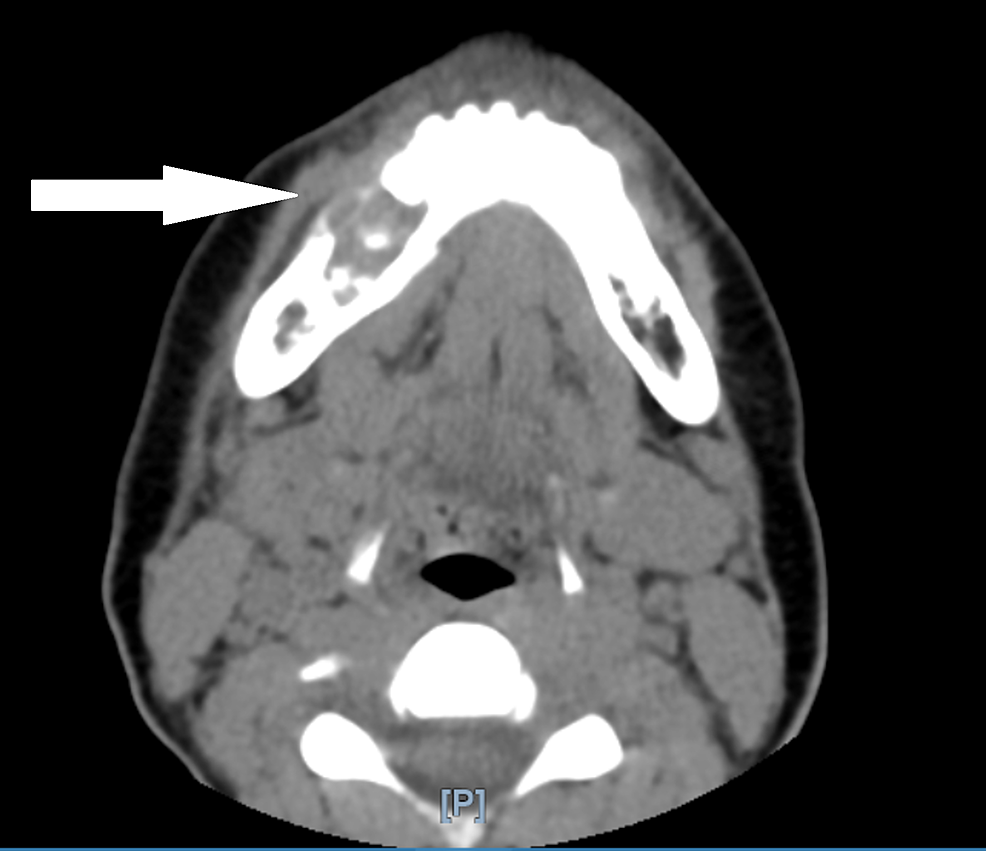
- At times when cancer specialists finds that there are multiple neck nodes or there are symptoms of cancer spread, cancer specialists advise patients to get PET scan to see for disease spread in other organs like Lungs and bones.
Treatment of Oral Cancer
- The best treatment of cancer of Lower Jaw and cheek is Surgery.
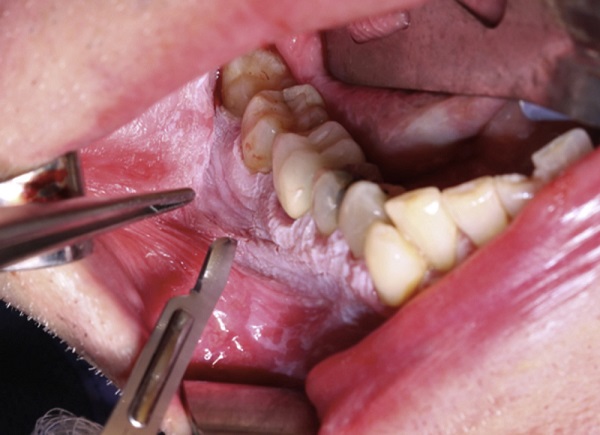
- During surgery, cancer Surgeon removes the disease along with 1cm margin of normal tissue all around the disease. Usually, the lymph glands on the same side of the neck are removed. This is called Neck Dissection.
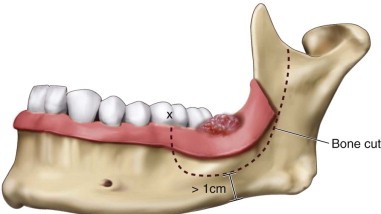
- When the part of lower jawbone is removed, it is called Mandibulectomy. Later the cancer surgeon or plastic surgeon will perform the reconstruction surgery to fill the gap.
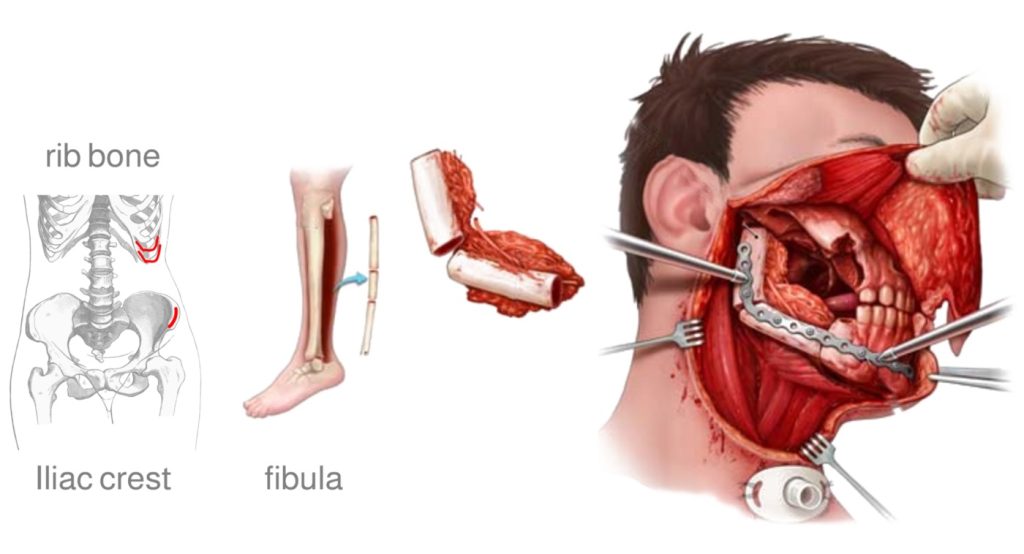
- There are two ways to reconstruct the defect after surgery. First, replace the gap with part of bone. This can be taken from Leg Bone (Fibula) or from bones of chest(ribs) or back (Scapula).
- The second option is reconstruction with Soft Tissues like muscle and fat with part of the skin. This is usually taken from Chest (pectoralis major flap), thigh (anterolateral thigh Flap), or skin below the chin(Submental Flap).
Recovery after Oral cancer Surgery
- Usually, patients are kept in ICU for a day after surgery. Patients are started on liquid diet via a feeding tube that goes from nose to stomach (Ryles Tube).
- Patient is asked to keep his mouth clean by doing gargles regularly. Slowly as the patient’s flap recovers, patient is encouraged to take oral liquids. The Ryles tube is removed 7-15 days after the surgery depending on patient’s tolerance to oral feeds and healing of the flap.
- Patients usually start taking full oral diet after 14-18 days of Surgery.
- Stiches in the neck are usually removed 14–18 days after surgery.

Rehabilitation after Oral Cancer Surgery
- Mouth opening Exercises(Jaw Stretcher)- This is usually started after 3-4 weeks after surgery in patients who have reduced mouth opening after surgery. These exercises need to be performed at least 10-20 times per day for a minimum of 2 years after surgery.
- Shoulder Exercises– Patients are taught shoulder overhead abduction exercises after 1-2 days after surgery so that they can have full range of motion.
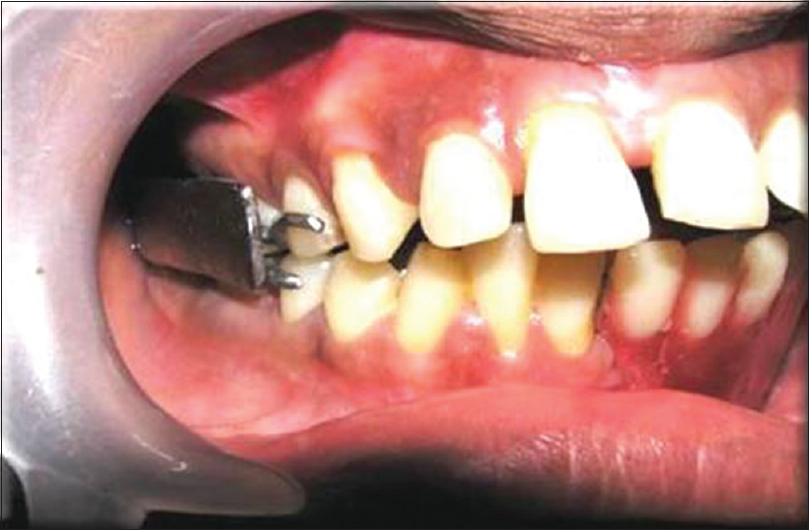
- Bite Guide Prosthesis- After oral cancer Surgery, there might be malalignment of upper and Lower Jaw which can make chewing difficult for the patients. Hence, a Bite guide Prosthesis is made for these patients which help them in chewing food after surgery.
Chemotherapy in Oral Cancer treatment
- Patients with advanced cancer of the jaw especially in cases where surgeon sees that disease has spread to areas where achieving a negative margin would be difficult, i.e. swelling extending above cheek bone, such cases are usually given chemotherapy first (Neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and then reassessed for response. If the disease responds well, then patient is advised to undergo Surgery.
- Apart from this, patients who had disease spread outside Lymph nodes (Extra nodal Extension) on final histopathology report, are given chemotherapy along with radiation therapy for better disease control.
- Patients with recurrent diseases which are not amenable to surgery are advised Chemotherapy.
- Patients with disease spread to other organs like lungs & bones are given chemotherapy or Immunotherapy.
Radiation therapy after Surgery
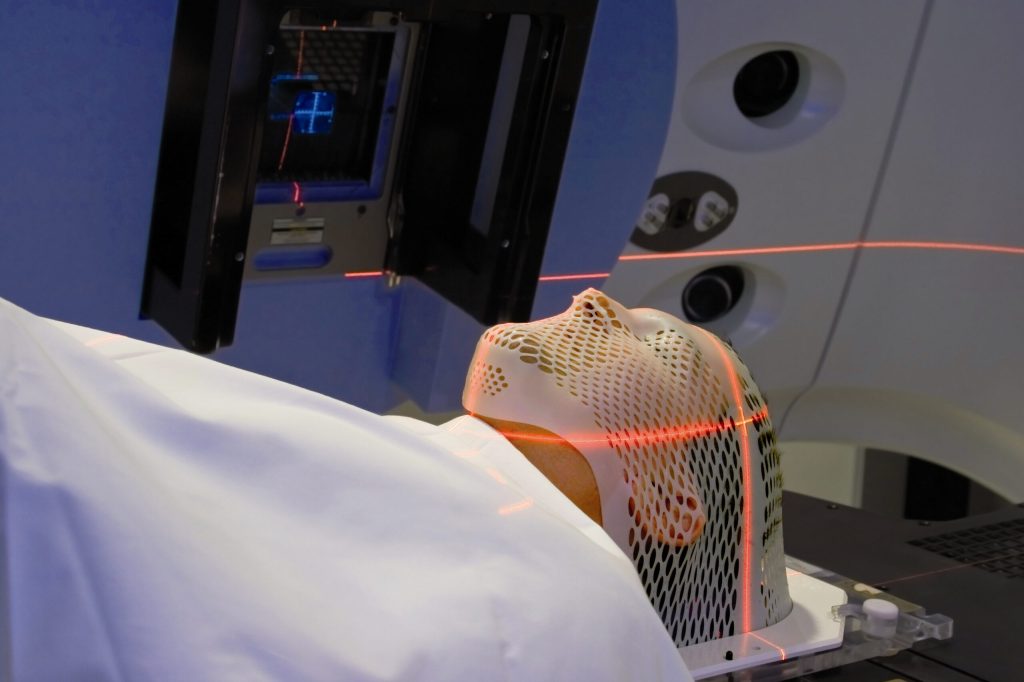
- Usually, patients with disease in stage III or Stage IVA or IVB are given radiation therapy after Surgery. Radiation therapy reduces risk of disease coming back (recurrence) after surgery and improves survival of patients.
This is usually started after 4–6weeks from surgery when the wound has completely healed. Radiation therapy is given for 5 days a week for roughly 6 weeks (30 to 33 sittings).
Side effects of radiation therapy
- The main side effect of radiation therapy is Mucositis. It means the inner lining of mouth gets small ulcers and gets swollen up because of which patient finds it difficult to swallow. Patients are usually given syrups to anesthetise the inner lining so that they find swallowing less painful. Patients are advised to take more liquid or soft blended diet while they are undergoing radiation therapy.
- Darkening of the skin.
- Dryness of mouth (Xerostomia)- Radiation therapy reduces saliva production causing dryness of the mouth. Patients are encouraged to take more liquids with food. At times, artificial saliva sprays are given to help in swallowing.
- Loss of taste and inability to tolerate spicy foods
Follow up after treatment
- Patients are advised to visit their cancer specialists every 3months for first two years and then every 6months for 5years. The interval is then increased to once a year. This is important as effects of tobacco are present in other parts of oral cavity leading to possibility of second cancers and recurrence of the disease.
- During follow up, cancer specialists do a thorough examination of mouth and neck to see for any abnormal areas around the surgical site or in rest of the mouth. If there are any abnormal areas, then a biopsy from that area is taken and correlated with CT scan or MRI to know the deep spread of disease.
Recurrence of Oral cancer
- Oral Cancer especially in advanced stage can come back. The usual time period of recurrence is generally first two years after surgery but it can come back after many years after surgery.
- Patients with cheek or jaw cancer usually have chewed tobacco or consumed alcohol for a significant years before they develop cancer. The inner lining of the mouth which was earlier normal can develop second cancer due to previous injury from tobacco (Field Cancerisation). Hence, all patients are advised to regularly follow up with their cancer specialists so that the second cancers can be identified at a very early stage.