Introduction
Thyroid Gland are paired glands (two lobes) that lie in front of our windpipe and secrete a hormone called Thyroxine which help maintain our normal body temperature as well our activity level.
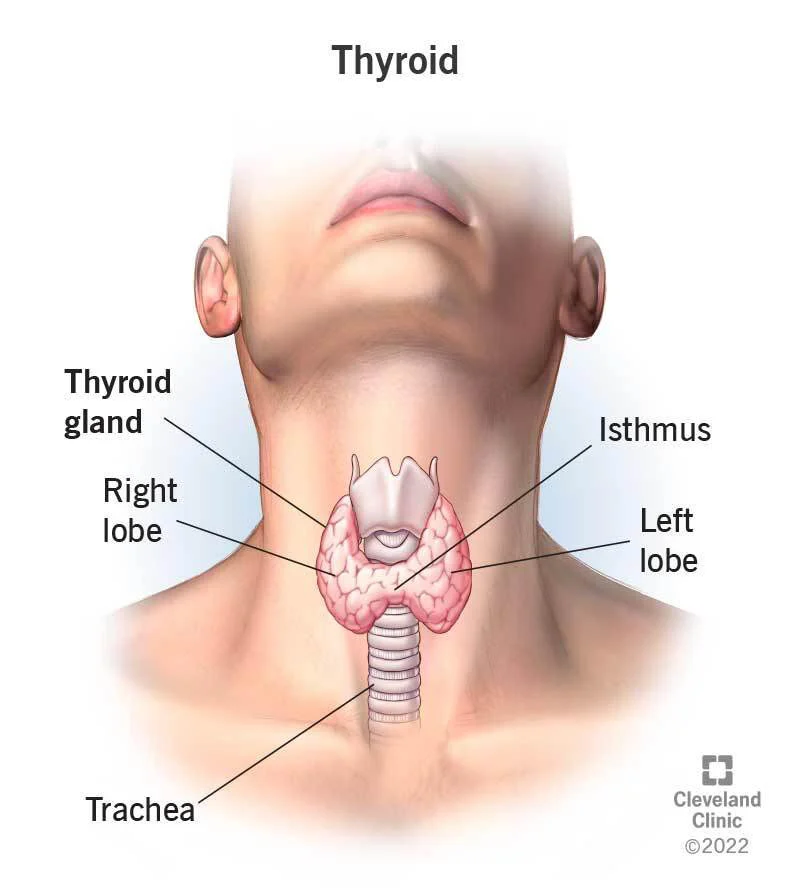
Thyroid Swellings
- Thyroid swelling or Nodules are small bumps present over one or both the thyroid lobes. Sometimes, they can grow large to involve the entire thyroid gland.
- They are quite common in general population especially in females and if everyone gets a Sonography of thyroid gland, at least 2 out of 10 people will have nodules in their Thyroid Glands.
- Well, the good news is that most of these nodules do not need any intervention. They are usually painless and small in size.
- When these nodules grow larger enough to become visible, then the patient notices them.
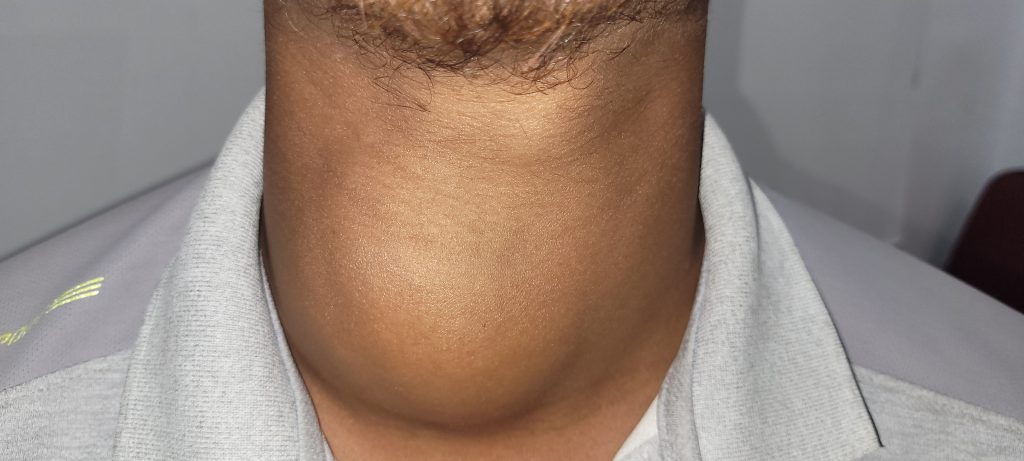
Warning Signals for Thyroid Swelling
- Thyroid Swellings that are visible to the person standing at some distance need evaluation.
- Those associated with swelling in other part of Neck (Lymph Nodes) like the sides of the neck or if they are multiple and in both the lobes(Multinodular Goitre).
- Thyroid Swellings causing symptoms like intermittent choking sensation while swallowing and breathlessness especially on Lying down and wake the person in the middle of the night. These are red alert symptoms that these people need to see an expert as soon as possible and get evaluated.
- Sometimes, Thyroid nodules can produce excess thyroid hormones leading to symptoms of Hyperthyroidism.
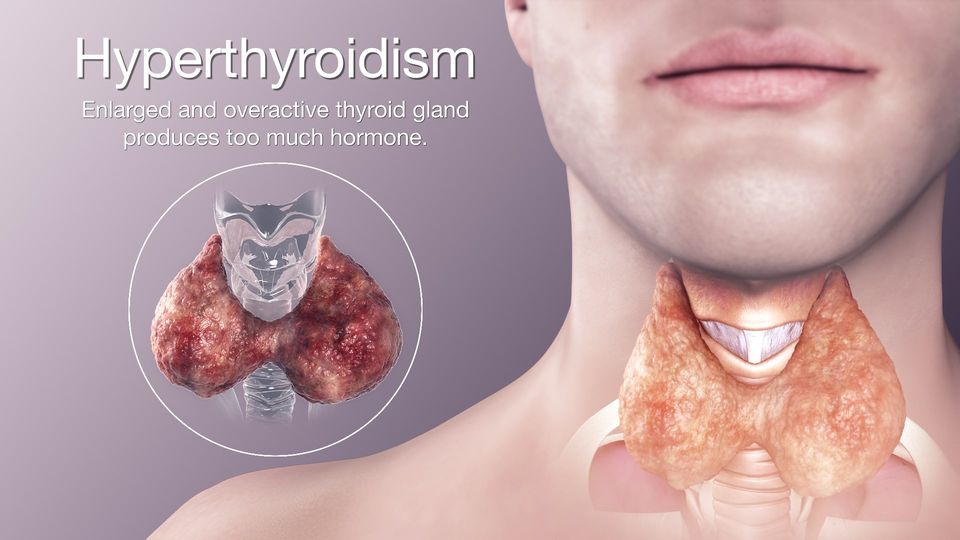
Symptoms of Increased or Decreased Thyroxine Levels (Hyperthyroidism/ Hypothyroidism)
- Abnormal increase in Thyroid Hormone levels (Hyperthyroidism) can produce symptoms like excessive sweating, palpitations, tremors of hands, bulging of eyes, unintentional weight loss, increased appetite despite eating adequate diet and irregular menses in females.

- Those associated with abnormally low levels of thyroid hormones(hypothyroidism) in the body which lead to weight gain, lethargy, hair loss, swelling over face or feet & face and irregular menses.

Tests for Thyroid Swellings
- When a patient comes with any of the above symptoms, we reassess all these symptoms and clinically see the size of swelling in the neck. The patient is advised to get a Thyroid function test(TFT) to evaluate if there is any increase or decrease in thyroid hormone levels.

- Once we see that thyroid functions are normal, we ask them to get a Sonography(USG) of the thyroid gland where we see for various features of these swelling and the radiologist tells us the relative chances of it being an abnormal or normal swelling. This is graded according to a score called TIRADS(Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data system).
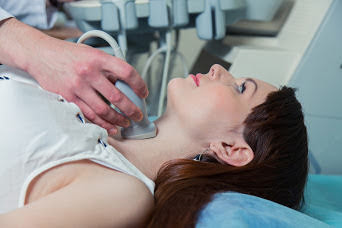
- The swelling which is larger than 2cm or have abnormal features is subjected to a small needle aspiration test called Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). It is best done under Sonography guidance where the radiologist pricks a small needle into the swelling and takes out few cells and sends it to the pathologist for examination.
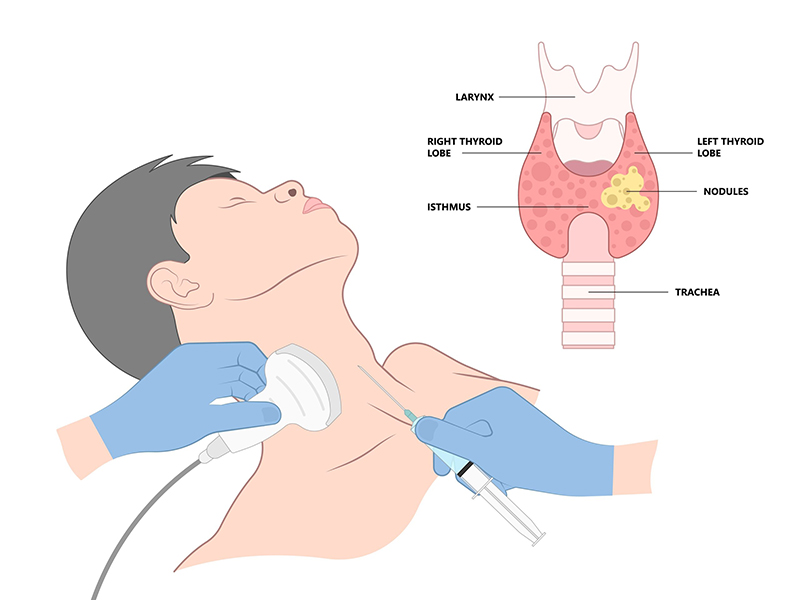
Treatment of Thyroid Swellings
- Thyroid swellings which have no abnormal features and/or smaller are best observed with regular sonography at 6-12months interval.
- If there are any abnormal features in the sonography or FNAC, the patient is advised Surgery.
- During Surgery, Surgeon removes the affected gland or both lobes of Thyroid gland.
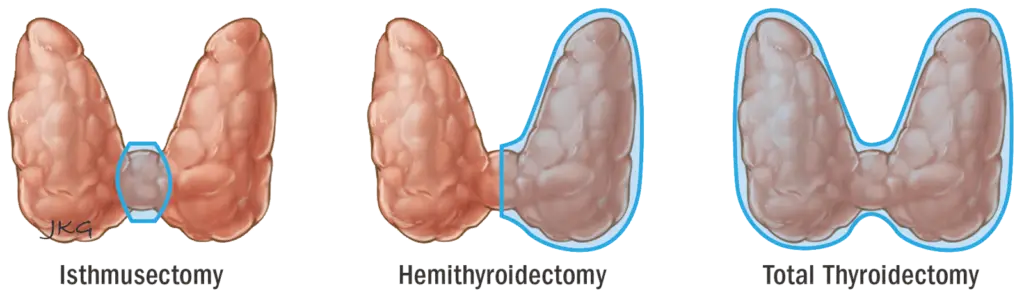
- If only affected or one lobe is taken out then it is called Hemithyroidectomy. If the nodules are on both sides or if there is any suspicion of cancer, both the lobes of thyroid glands are removed (Total thyroidectomy).
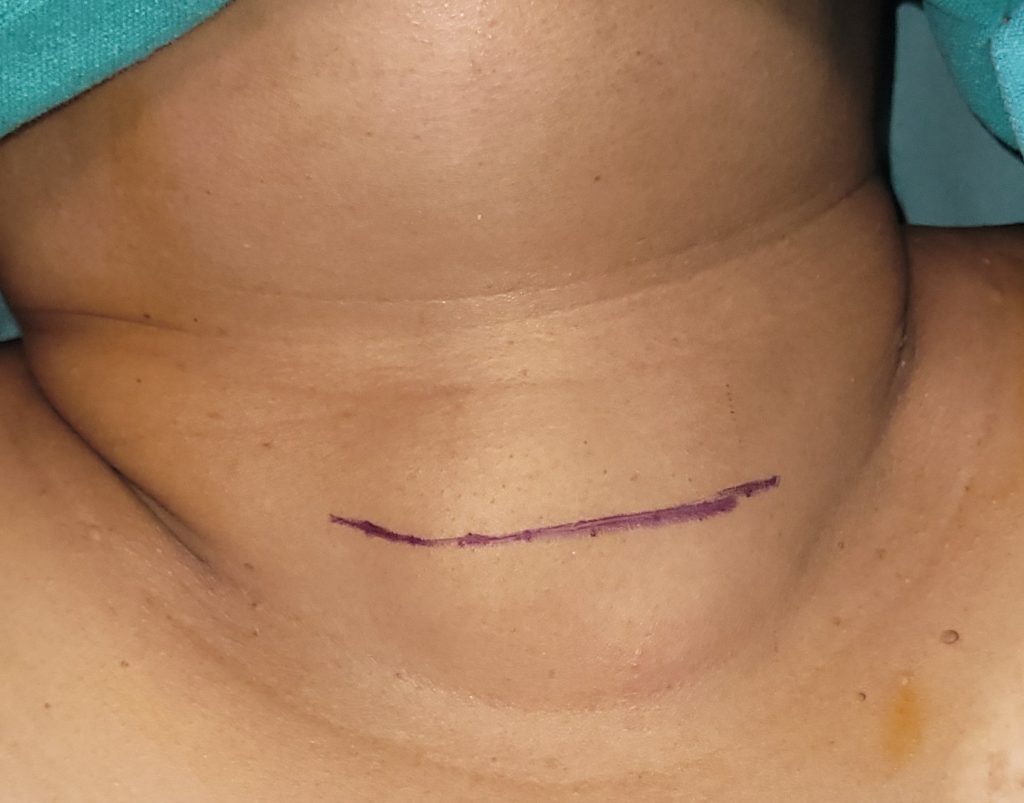
- Surgery is done under General Anaesthesia through a small incision in the neck that usually blends with neck crease.
Complications of Thyroid Surgery
- Bleeding- Thyroid gland is extremely vascular & has multiple small blood vessels supplying it which can cause bleed during the surgery.
- Voice change– The nerves which are responsible for voice production (recurrent laryngeal nerves) are close to the Thyroid gland and lie in the space between windpipe & food pipe (Tracheoesophageal groove). They may get inflamed during dissection causing temporary or permanent damage to the nerves.
- Need for Calcium Supplements-The glands responsible for calcium regulation(Parathyroid Glands) in the body are located just behind the Thyroid glands and may get damaged during the dissection which may lead to low calcium levels(hypocalcemia) causing a condition called Tetany. The first symptoms are tingling & numbness around the face and hands. If calcium levels is very low, there may be clawing of the hands(Carpopedal spasm).
- Need for Thyroxine Supplements– After removal of both or one Thyroid lobe, patient may need Thyroxine supplements. The patient needs to take the medicine on empty stomach. These do not have any side effects but patient nay need to get Thyroid function at 3months interval to adjust the required dosage.
- Scar in the neck– Thyroid glands are usually taken out through a transverse incision along the neck crease which produces a scar in the neck.
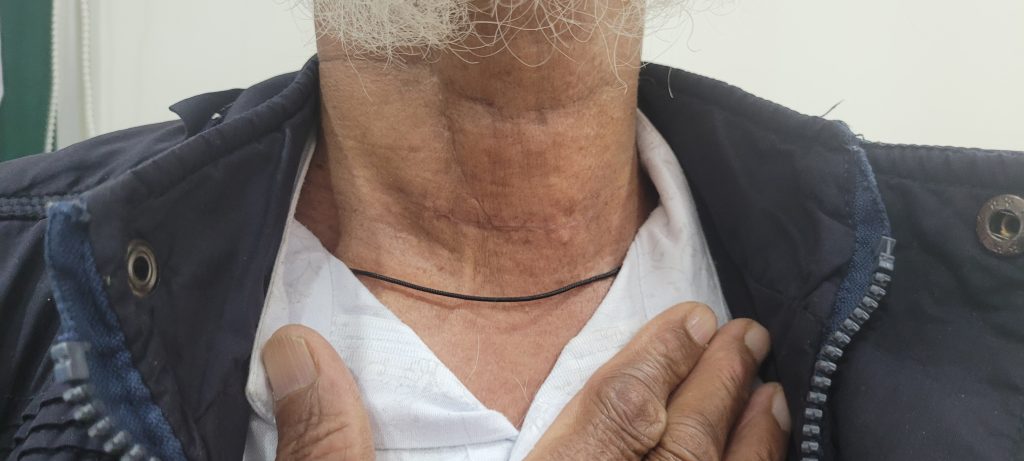
Course in the Hospital after Thyroid Surgery
- The patient is operated under General Anaesthesia and the tube is removed (extubating) in the operation theatre itself. Patient is kept under observation for half an hour in the recovery room.
- The patient can be allowed to have soft diet on the day of surgery after 4-6 hours and full diet from the next day of Surgery.
- The patient can be discharged on first or second post operative day after removing the drainpipe and checking serum calcium levels.
- The patients may be advised to take calcium supplements and Thyroxine tablets depending on the extent of the surgery
Adjuvant treatment after surgery
- The patient who undergoes surgery for Thyroid Cancer especially Papillary Carcinoma or Follicular carcinoma may need radioiodine therapy after 6-8 weeks of Surgery.
- The patients is advised to take iodine free diet and withhold any Thyroxine supplements that they may be taking.
- This is usually decided after getting serum Thyroglobulin (Tg levels) and antithyroglobulin (AntiTg) antibodies and low dose Radioiodine scan done after 6 weeks of surgery.
- The Radioiodine therapy(RAI) is done by giving the patient a special form of Iodine (I131). This gets absorbed in the remnant Thyroid tissue or microscopic disease left behind after surgery. Patients are usually kept in Isolated rooms for a day after therapy.
- The therapy does not have side effects like radiation therapy & is safe.
- The role of Radical radiotherapy or chemotherapy is limited in Thyroid Cancer & is reserved for inoperable cases or patients who are unfit for surgery.
- You can understand more about thyroid swellings through our video link-https://youtu.be/gtmEab-qbGk